mf_get_pal builds sequential, diverging and
qualitative color palettes.
Diverging color palettes can be dissymmetric (different number of colors in
each of the two gradients).
Usage
mf_get_pal(
n,
palette,
alpha = NULL,
rev = c(FALSE, FALSE),
neutral,
breaks,
mid
)Arguments
- n
the number of colors (>= 1) to be in the palette
- palette
a valid palette name. See hcl.pals to get available palette names. The name is matched to the list of available palettes, ignoring upper vs. lower case, spaces, dashes, etc. in the matching.
- alpha
an alpha-transparency level in the range [0,1] (0 means transparent and 1 means opaque)
- rev
logical indicating whether the ordering of the colors should be reversed
- neutral
a color, if two gradients are used, the 'neutral' color can be added between them
- breaks
a vector of class limit
- mid
a numeric value use to divide the palette in two colors
Examples
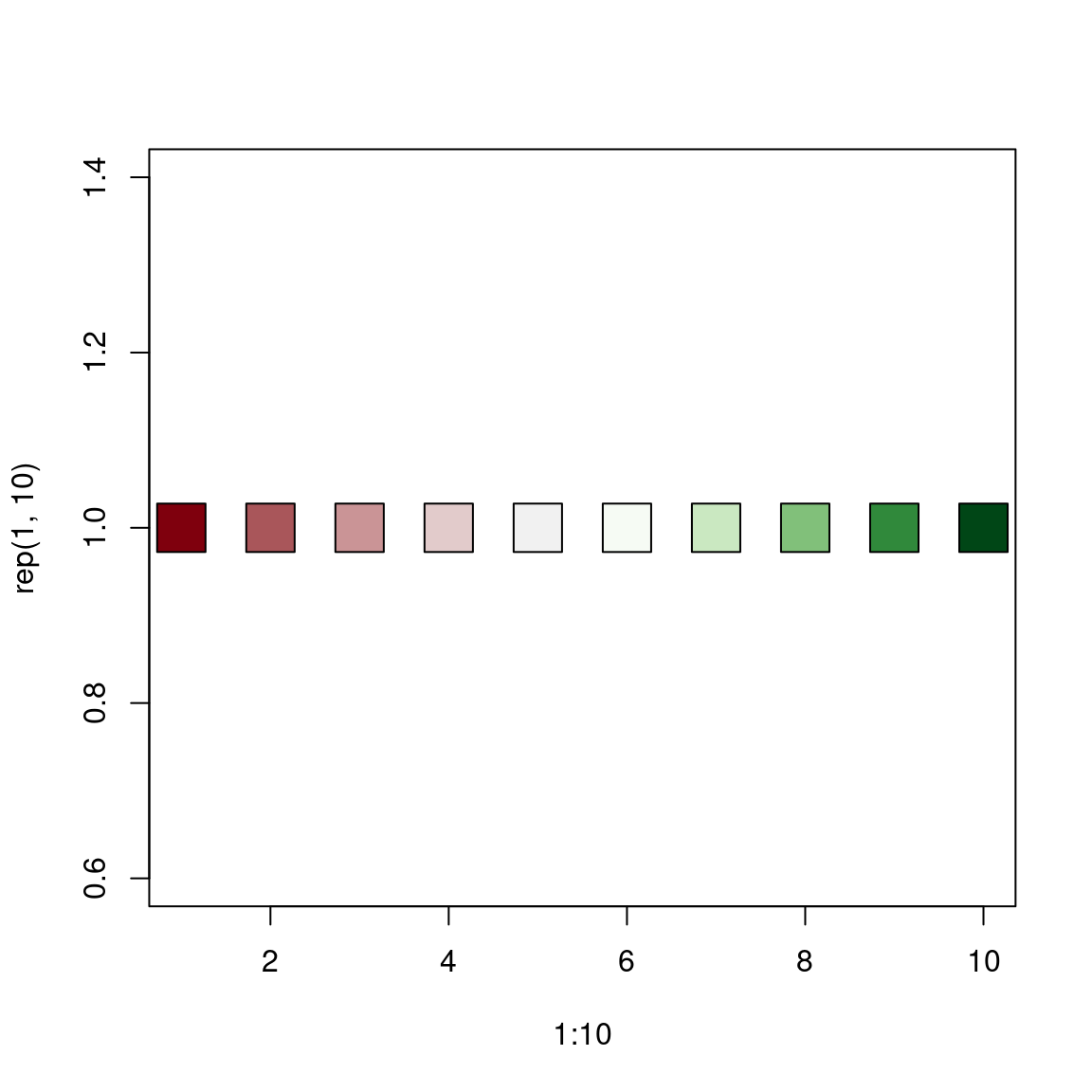
cls <- mf_get_pal(n = c(3, 7), palette = c("Reds 2", "Greens"))
plot(1:10, rep(1, 10), bg = cls, pch = 22, cex = 4)
 mtq <- mf_get_mtq()
bks <- mf_get_breaks(mtq$MED, breaks = "equal", nbreaks = 8)
pal <- mf_get_pal(
breaks = bks, mid = 15000,
palette = c("Dark Mint", "Burg"), neutral = "grey90"
)
mf_map(mtq, "MED", "choro", breaks = bks, pal = pal)
mtq <- mf_get_mtq()
bks <- mf_get_breaks(mtq$MED, breaks = "equal", nbreaks = 8)
pal <- mf_get_pal(
breaks = bks, mid = 15000,
palette = c("Dark Mint", "Burg"), neutral = "grey90"
)
mf_map(mtq, "MED", "choro", breaks = bks, pal = pal)
 pal <- mf_get_pal(breaks = bks, mid = bks[4], palette = c("Dark Mint", "Burg"))
mf_map(mtq, "MED", "choro", breaks = bks, pal = pal)
pal <- mf_get_pal(breaks = bks, mid = bks[4], palette = c("Dark Mint", "Burg"))
mf_map(mtq, "MED", "choro", breaks = bks, pal = pal)